What Is Blockchain?The Transformative Technology
“A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network's nodes.” - Investopedia.com
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain works by grouping transactions into 'blocks' that are connected in a chain using cryptography. This chain of blocks is distributed across a peer-to-peer network of participants known as nodes. Each block contains a timestamp and a link to the previous block, creating an immutable sequenced record of all transactions on the network from its inception.
Because this distributed ledger is not stored in any single location and transactions can only be added with consensus from nodes, blockchain provides increased transparency and data integrity. Any unauthorised attempt to alter or delete transactions would be detected and rejected by the network. Through the cryptographic linking of blocks, duplication is eradicated while security is bolstered. By facilitating cooperative yet secure record keeping between parties who may not fully trust one another, blockchain possesses the power to restructure how commercial and social systems are structured.
This article provides a moderate expanded guide to blockchain, detailing how this pioneering technology operates, the primary categories of blockchain networks, its diverse scope of uses across sectors and the revolutionary advantages it can supply, as well as investigating difficulties that must be tackled along with what potential the longer term could maintain for blockchain.
How Blockchain Technology Works?
A blockchain network consists of a shared database or ledger that is distributed across multiple participants known as nodes. These nodes can be located anywhere in the world and participate in administering the network. When a new transaction occurs, it is broadcast to all the nodes in the network. The nodes then validate the transaction according to pre-defined consensus rules. Once a majority of nodes reach consensus that the transaction is valid, it is approved and a new block is created containing that transaction and other transactions waiting to be approved.
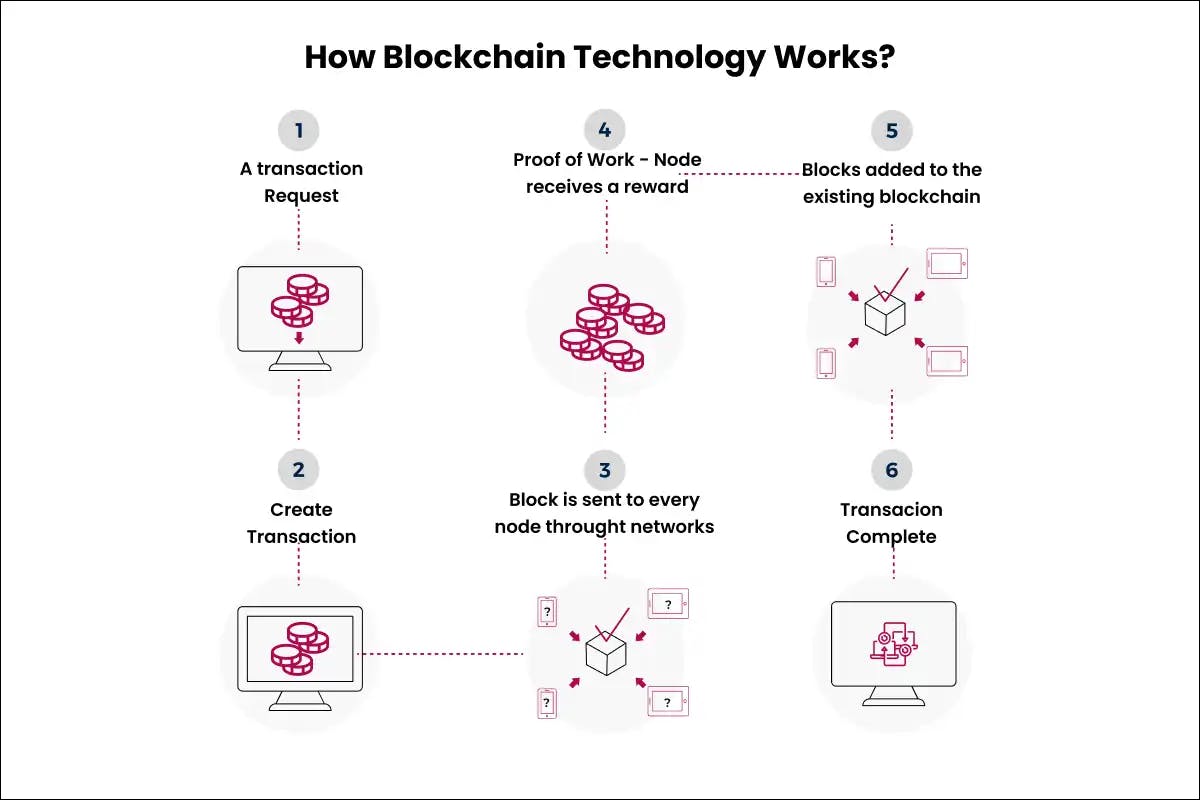
Each block has a timestamp and a unique cryptographic hash that links it to the previous block, creating an unalterable chain. If anyone attempts to modify an earlier transaction, the hash of that block will change and break the chain. This tamper-evident property ensures the integrity of the ledger since any unauthorised changes would be immediately detected by the network.
Key Attributes of Blockchain Technology
Some key attributes of blockchain technology are:
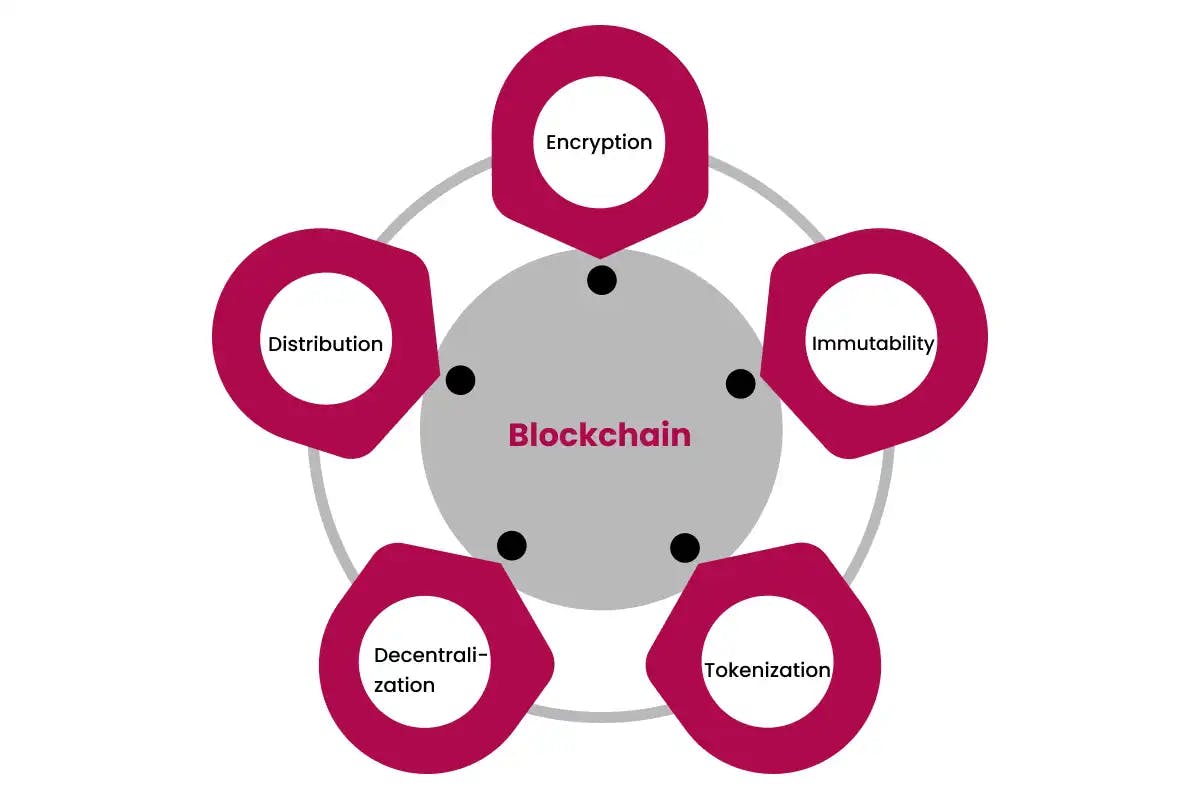
Decentralised
There is no central administrator or centralised data storage. The network is administered by a peer-to-peer network of nodes that all have identical copies of the ledger. This eliminates single points of failure.
Transparent
All participants in a blockchain network can view transaction history but the identity of users is pseudonymous. This provides transparency while retaining privacy.
Immutable
Transactions, once recorded on the blockchain, cannot be altered or deleted. This permanency is critical for accurate record-keeping.
Cryptographically Secure
Transactions are validated through cryptography mechanisms such as hashing and digital signatures. This math-based security ensures authenticity and integrity.
Consensus-Driven
Nodes agree on whether transactions are valid according to consensus protocols. Common protocols include proof-of-work, proof-of-stake, and practical Byzantine fault tolerance.
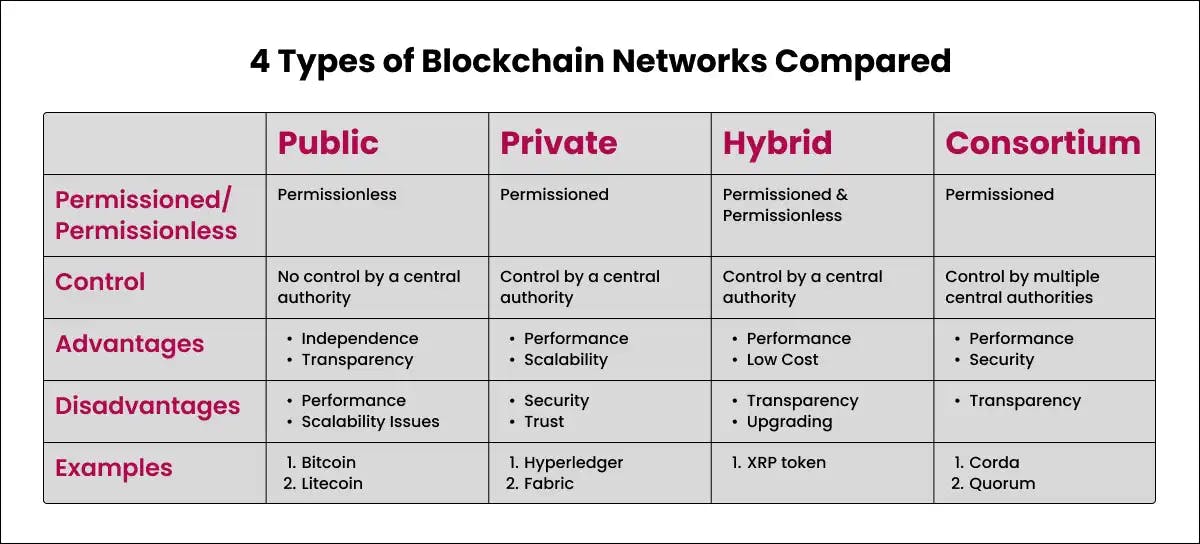
Types of Blockchain Networks
There are several types of blockchain networks, each with its advantages and trade-offs:
Public/Permissionless
These are open networks where anyone can join, participate, and view transaction histories. Public blockchains often use native cryptocurrencies as an incentive for validating transactions. Bitcoin is the most well-known public blockchain. While transparent, public networks sacrifice privacy.
Private/Permissioned
These limit participation to a set of known, identified participants. Read and write permissions may also be restricted. Hyperledger Fabric is an excellent example of a private blockchain used primarily for enterprise applications. Permissioned networks provide more control but are less decentralised.
Consortium
A consortium blockchain is shared between a pre-selected set of organisations to facilitate transactions within an industry or use case. R3's Corda is used by banks for inter-bank transactions. Consortium blockchains strike a balance between openness and control.
Hybrid
Hybrid architectures aim to bridge public and private blockchains. They allow integration of the immutability and transparency of public chains with the control and privacy of permissioned chains.
Potential Use Cases of Blockchain
Given its attributes of immutability, transparency, security and disintermediation, blockchain technology has emerged as a disruptive innovation with a broad range of applications across multiple industries:
Financial Services
Blockchain is seeing early adoption for payment processing, trade finance, KYC/AML checks, clearing and settlement of securities, and other applications by banks, insurers and capital markets.
Supply Chain
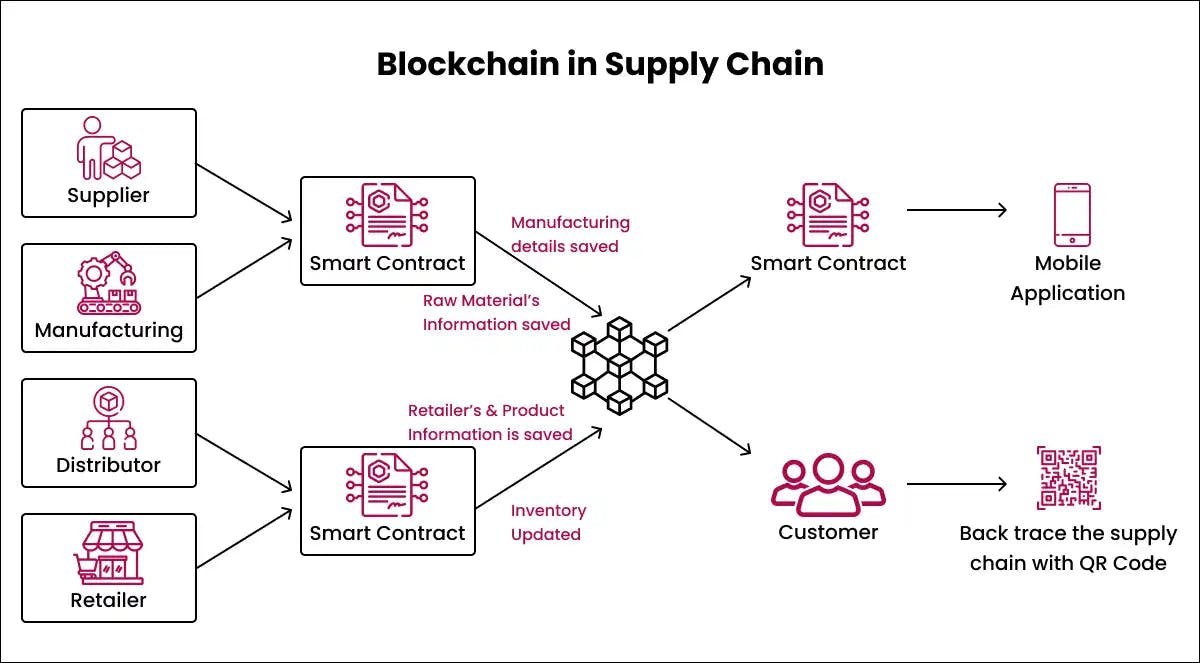
Blockchain enables highly secure provenance tracking of goods and materials from origin to destination. This technology is being used to enhance traceability and prevent counterfeiting.
Healthcare
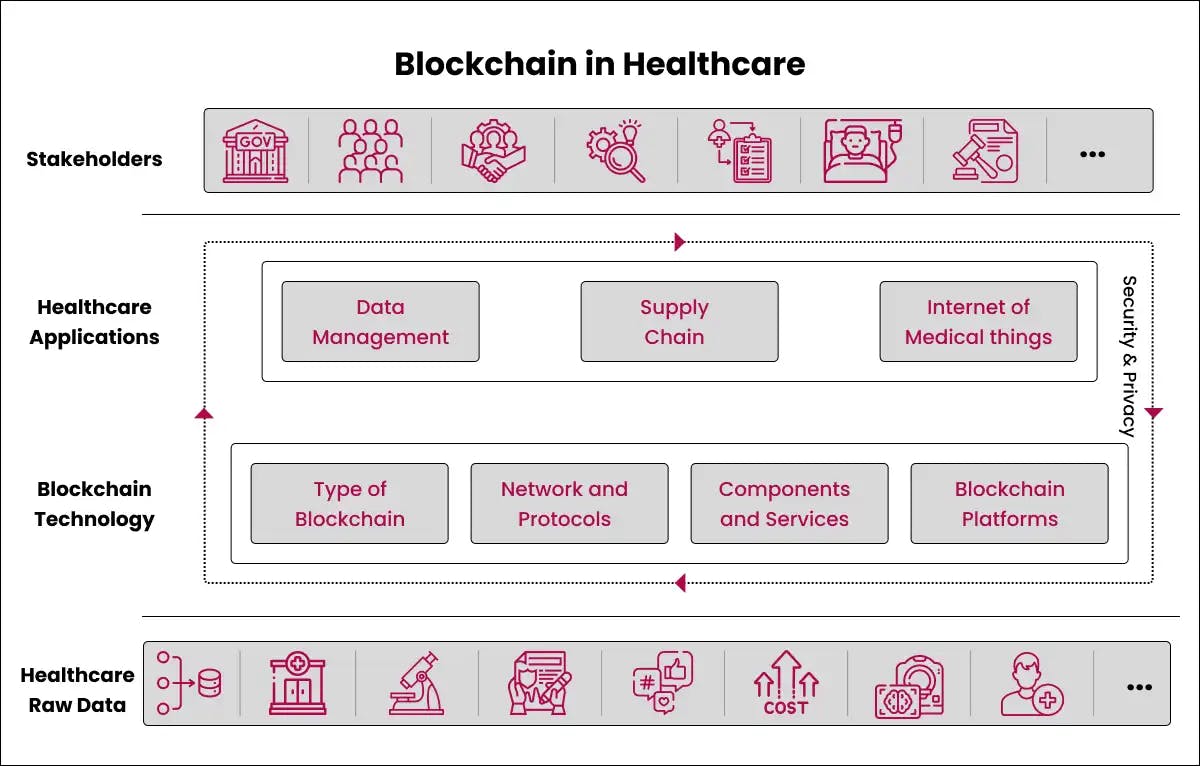
Securely sharing medical data is a major use case for blockchain in healthcare. Securely sharing medical data is a major use case for blockchain in healthcare. However, Blockchain technology also facilitates users with the secure transfer of medical records, helps to manage supply chains, and so forth.
Real Estate
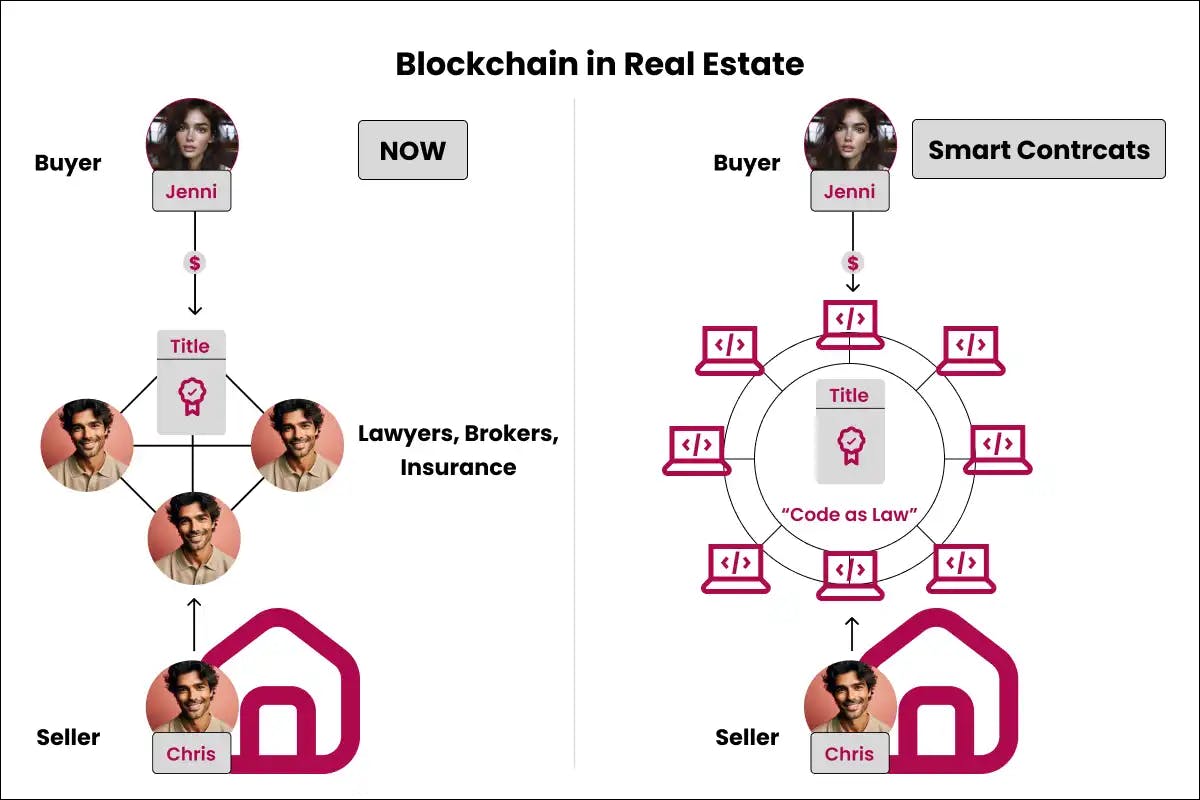
Blockchain can create immutable property title registries to prevent fraudulent title claims and ownership disputes. It also enables automation of rent and utility payments through smart contracts.
Media
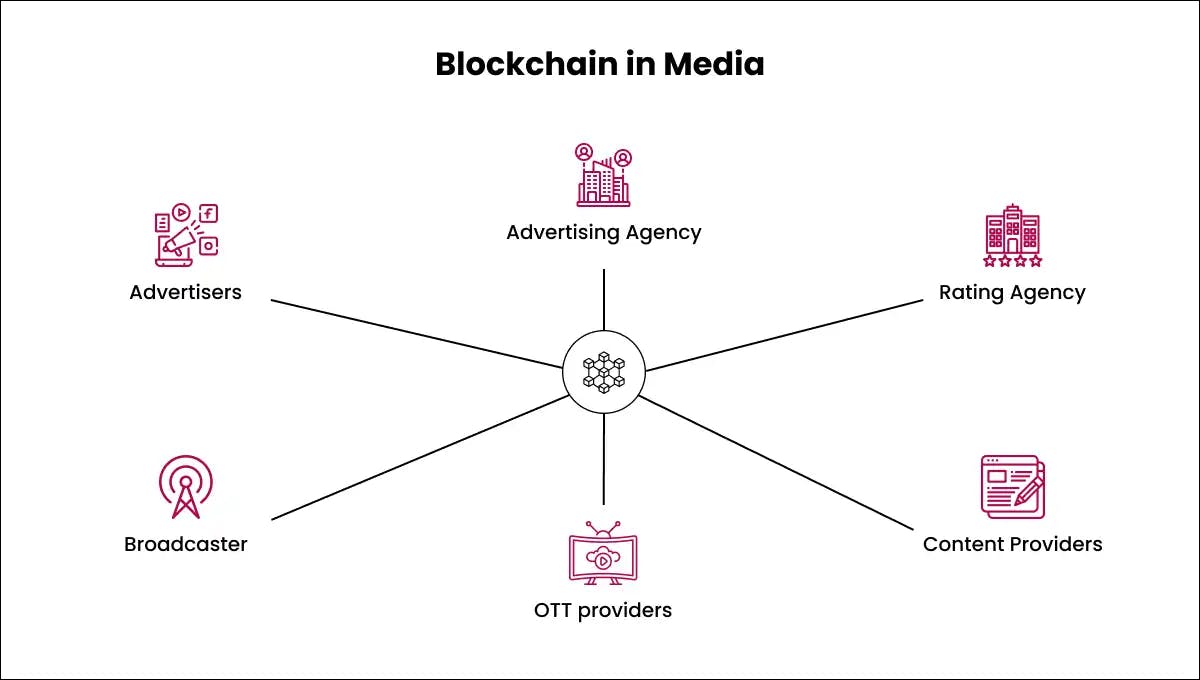
Blockchain assists with digital rights management and allows for quicker and more transparent distribution of royalty payments according to utilisation.
Key benefits of blockchain
Enhanced transparency and Audibility of transactions
The immutable ledger provides a verifiable history of all transactions. This improves internal and external auditing.
Increased Trust
Disintermediation and use of consensus eliminate the need for third-party validations. Smart contracts automate rule-based transactions.
Improved Security
Cryptography, resilience against outages, and elimination of central points of failure greatly enhance security.
Faster Processing
Decentralised validation enables faster settlement by reducing reconciliations and intermediary steps.
Lower Costs
Redundant processes are eliminated while automation through smart contracts reduces manual efforts.
Blockchain Technology is The Future!
For many industries, blockchain technology promises significant development through bolstered transparency, fortified security, augmented automation, and optimised efficiency in multi-step interactions. Though widespread everyday use is still some time off, acceptance is quickening as the technology advances. If key hurdles can be overcome, blockchain may conduct the next surge of digital change across numerous domains.
For years now, the technology of blockchain has continued advancing, causing many companies to look for the right partners to help them maximise what this innovative disruption can do. One team paving the path ahead is Codiste, a top blockchain development company. With their unmatched background designing and implementing customised blockchain systems within diverse industries, Codiste distinguishes itself as an extraordinary partner.
Codiste has extensive experience in the blockchain field, having completed over fifty significant projects. Through employing their technical expertise and strategic vision, Codiste, being a reliable blockchain company in USA, assists organisations in applying blockchain to bolster transparency, trust, automation and efficiency across various situations.