


In the coming days, cyber-attacks are in all probability going to rise exponentially. Even the most efficient systems have been attacked in recent times. Governments, corporate entities, and individual citizens were affected because of this. That is when quantum cryptography comes into the picture. In a world where data breaches take place daily, a tech startup created a quantum encryption system that is thought to be impenetrable.
A renowned government agency decided to deploy QuantumSec's latest encryption for a top-secret mission. Their communications were secure, due to the quantum encryption protocols, or so they thought. As the operation unfolded, the agency's encrypted channels began to experience strange glitches. Intercepting quantum particles shouldn't have been possible without detection, yet something seemed off. The agency quickly realized that while their messages were secure, an unseen adversary had discovered a way to manipulate the quantum communication channel itself—causing a ripple in their encryption system without technically "hacking" it.
This unexpected twist left the agency questioning: if quantum cryptography is the future of security, how did things go wrong? The answer lay not in the encryption itself but in understanding the intricate and evolving nature of quantum cryptography.
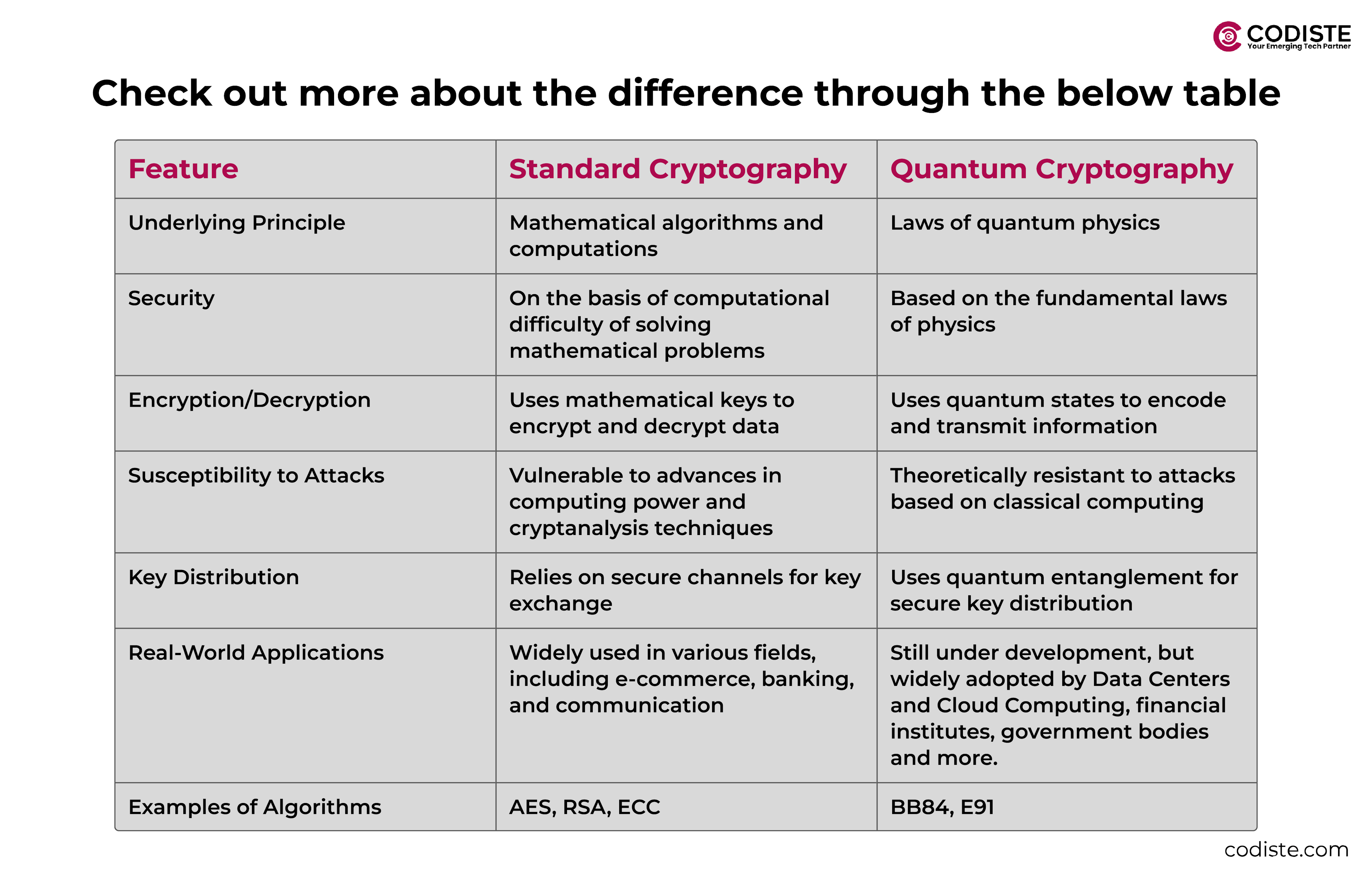
Quantum cryptography is a new technology that uses quantum mechanics principles to establish secure communication. Traditional cryptography often implements arithmetic algorithms to do the job of data encryption and decryption. Quantum cryptography, on the other hand, employs the quantum laws of nature (which prevail at the atomic and subatomic levels) to secure data, hence making it virtually impossible to intercept or hack without detection.
Quantum cryptography is rooted in the concept of creating a quantum key distribution (QKD) - especially the BB84 protocol by Charles Bennett and Gilles Brassard back in 1984. The first is a QKD system which allows two parties to create secret keys by sending quantum particles (photons) to each other.
Quantum particles cannot be measured or observed without altering their state, so if a third party tries to listen to the communication, the particles will be disturbed and the communicators will be alerted to the breach. This inherent feature of quantum mechanics is what ensures a high level of security.
Quantum cryptography highlights the way of securing the transmission of the keys used for encryption and decryption. Usually, the data itself is protected by traditional cryptographic methods, but the keys exchanged over quantum channels are impossible to eavesdrop on—a monumental step forward for the confidentiality of sensitive communications.
Traditional cryptography uses the complex operations of mathematical algorithms to guarantee its security. The assumption is that the security of these setups lies in the fact that the computational tasks needed for factoring are very large. Often the time required for this can be measured in years and even centuries.

As an example, the RSA encryption algorithm essentially hinges on the difficulty of factoring large prime numbers, and this is something that classical computers still cannot solve excellently. But the real threat comes in the form of the progress in computer power—mainly due to the idea of quantum computers yet to come—which is making classical algorithms more susceptible to being broken. Suppose a quantum computer is strong enough; then (theoretically) solving the problem of RSA, it should take no more than a few minutes.
On the other hand, quantum cryptography is not built on the complexity of the conventional methods of mathematics but rather on the fundamentals of quantum mechanics, the rules of which are immutable. Quantum cryptography by law offers security that is certain only through the laws of physics. No matter the computational power used, a third party cannot listen in to a quantum key distribution channel without disturbing the quantum particles and revealing their presence. For this reason, quantum cryptography is an excellent solution for the securement of today's encryption and is also a viable option for later, under the actual threatening scenario of quantum computing that may overcome the outdated traditional methods.
Quantum cryptography has really taken off in the last few years, changing from mere theoretical ideas to real-life practical applications. Governments, financial institutions, and big companies are becoming interested in quantum encryption as a means of data protection. The very first time a quantum cryptography application was used in real life was in 2004. At that point, an Austrian bank securely transferred encrypted money by using quantum keys. After that, the research and development work sped up, and several quantum key distribution (QKD) networks were built worldwide.
Quantum cryptography has been recognized as a big game changer in recent years because of the development of quantum computers. With quantum computers increasingly living up to their ruthless timetables, they can take advantage of the weak points of the current encryption methods that would eventually make the systems unviable.
More and more people are taking notice of the fact that their information in cyberspace is getting more and more vulnerable and hence the issue of securing their information has become the most important thing. We have found that quantum-resistant techniques have been put at the top of the arena of institutions such as financial institutions, government agencies, and healthcare organizations. Moreover, the implementation of quantum cryptography to ensure data safety is the way to go for some companies.
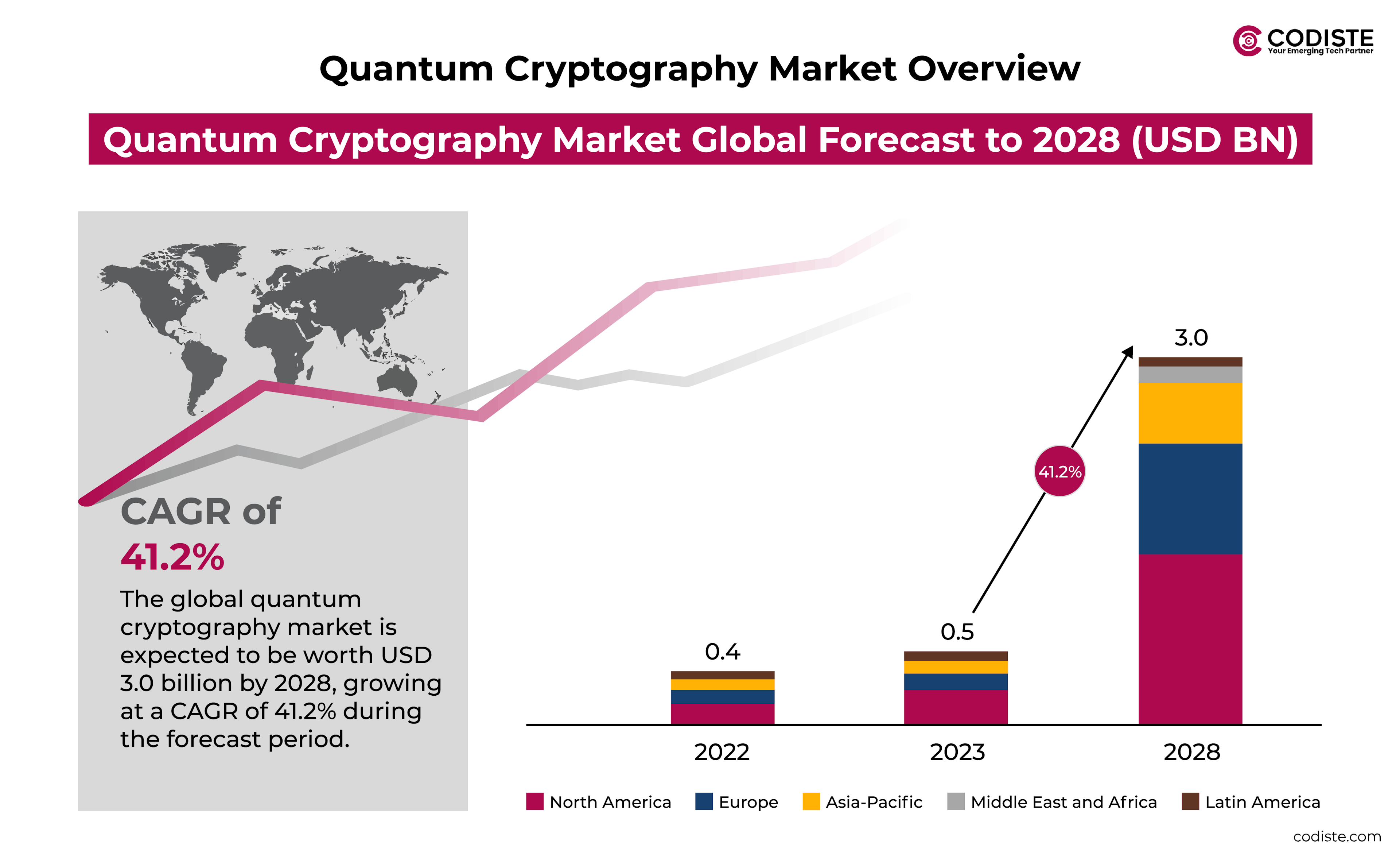
Furthermore, there is an increase in the supply of QKD solutions available from companies like ID Quantique and Toshiba, and thus, the adoption of quantum communication advances at a faster rate. The U.S. and China are two of the countries that have made the most significant progress in the secure implementation of quantum communication technologies. They have contributed greatly to the field by pouring in large sums of money. This in turn, further stimulates the technology's market penetration. The global quantum cryptography market is predicted to reach more than 3 billion by 2028 with an anticipated unprecedented growth as the technology would be more accessible to the end users.
Protect your data from cyberattacks with Codiste’s Quantum Technology.
The universe of cryptocurrency revolves around a multitude of factors including blockchain technology, digital currencies, and encryption techniques that are essential in securing information. While both concepts go hand in hand in securing information and the transmission of these types of information, quantum cryptography creates a clear line of demarcation between traditional cryptography and blockchain technologies in various important aspects.
On the one hand, it cannot be denied that quantum cryptography brings an unbeatable level of safety which is the characteristic of quantum particles. In contrast to the customary ways of encoding that are implemented by intricate mathematical formulas, quantum cryptography exploits the tangible features of quantum mechanics, which makes it immune to conventional decryption. This gap in security is the reason for its high worth in a world where quantum computers can overthrow conventional cryptographic algorithms.
Secondly, quantum cryptography addresses a problem that has influenced blockchain and digital currencies for a long time: ensuring the security of communication. Although blockchain is primarily known for its security features, the fact is that it uses outdated encryption methods, which were already discussed in the previous section, and hence, it can be easily attacked by future quantum computers.
By introducing quantum cryptography into the blockchain, we can bring about a major shift in security standards and thus, the latter will no longer be a headache in the future. No doubt, quantum cryptography can be seen as a game-changer in this field.
According to the experts, the future of quantum cryptography is very incredible, with the security, privacy, and communication of different areas affected by it. The most important thing, of all, will be its part in saving important infrastructure, such as financial systems, government networks, and healthcare data, from future cyber threats.
Since traditional encryption methods like RSA and ECC have run into a dead-end, they will soon be at great risk, when quantum computers step forward. Quantum cryptography is regarded as the antidote to these threats. It provides tough measures capable of surviving even the most cutting quantum attacks. The majority of specialists argue that quantum cryptography will be the main vehicle of secure communication in the coming decades, especially since quantum computing may go mainstream.
Moreover, quantum cryptography will be a very decisive factor for national security in the future. Most countries are spending a lot of money on this technology to fix security lapses in quantum communication to ensure that their military, intelligence, and critical communication networks remain secure in an era of rapidly deteriorating cybersecurity.
When it comes to commercial applications, institutions like banks, healthcare, and energy can use quantum cryptography by increasing the security of transactions, patient records, and operational data. On the other hand, providing such a kind of quantum cryptography is needed for quantum computing so that the technology is used even in the future.
We can expect even greater improvements in quantum cryptography protocols such as satellite-based QKD and the arrival of more efficient photon-based communication systems. The aim of these improvements is to make quantum cryptography more scalable, cost-effective, and widely used. It will also ensure that it will remain an integral part of the cybersecurity of the digital era in the future.
Quantum cryptography represents the latest and the most advanced way of delivering secure and foolproof communications. It relies on the laws of quantum physics to immunize even the smallest units of information from unauthorized access, interception, or modification. As we observe the rapid evolution of quantum computing with every passing day, it’s undeniable that conventional cryptographic systems have become more susceptible to new techniques and quantum methods. This leads to the need for the safety of information exchange, transactions, and other forms of data handling to a whole new level. It has become critical to adopt quantum cryptography much faster than we thought. Applications of quantum cryptography can be seen in various fields, with solutions implemented in finance, banking, telecommunications, infrastructure protection, and government sectors.
Businesses and organizations that want to be ahead are not just making quantum cryptography a choice but rather a necessity. Companies such as Codiste, are the best place to go when the goal involves the introduction of secure, scalable, and future-proof quantum cryptography solutions in your organization. Codiste, one of the reliable quantum cryptography providers of original cryptographic solutions, is responsible for tight security and protecting your data in an age of increasing quantum phenomena. Irrespective of your company's size, be it a large corporation or a small business, the team of Codiste's experts will support you in this unpredictable area of technology and secure your most loved businesses.Contacts Us



Every great partnership begins with a conversation. Whether you’re exploring possibilities or ready to scale, our team of specialists will help you navigate the journey.