


As defined by Investopedia: “A blockchain is a distributed database or ledger shared among a computer network's nodes.”
Blockchain technology works by putting transactions together into groups called blocks. Then, these blocks are connected in a chain, and strong encryption keeps them safe.
This entire chain is distributed across a peer-to-peer network of participants, known as nodes. Each block contains important details: a timestamp and a cryptographic link to the previous block. This design creates an immutable, sequenced record of every transaction on the network, right from its very beginning.
Adding transactions to the ledger requires agreement from all the nodes in the network because the ledger is spread out and not kept in one place. This decentralized method makes things much more open and protects the integrity of the data.
Most nodes would promptly notice and reject any illegal effort to change or remove previous transactions.. The cryptographic linking of blocks effectively eliminates duplication while greatly strengthening overall security.
One of the best things about blockchain is that it lets people who don't completely trust each other keep records that are both safe and cooperative. This special power of blockchain could change the way many business and societal systems work.
This updated guide provides a clear yet detailed explanation of blockchain technology. It discusses its workings, the primary types of blockchain networks, a wide range of practical uses in various sectors, its revolutionary benefits, difficulties, and bright future.
The foundation of a blockchain network is a shared database or ledger that is dispersed across numerous users, referred to as nodes, who can be found anywhere in the world. These nodes work together to administer and maintain the network.
Every time a new transaction takes place, the network's nodes are all informed. The transaction is subsequently verified by each node using pre-established consensus procedures.
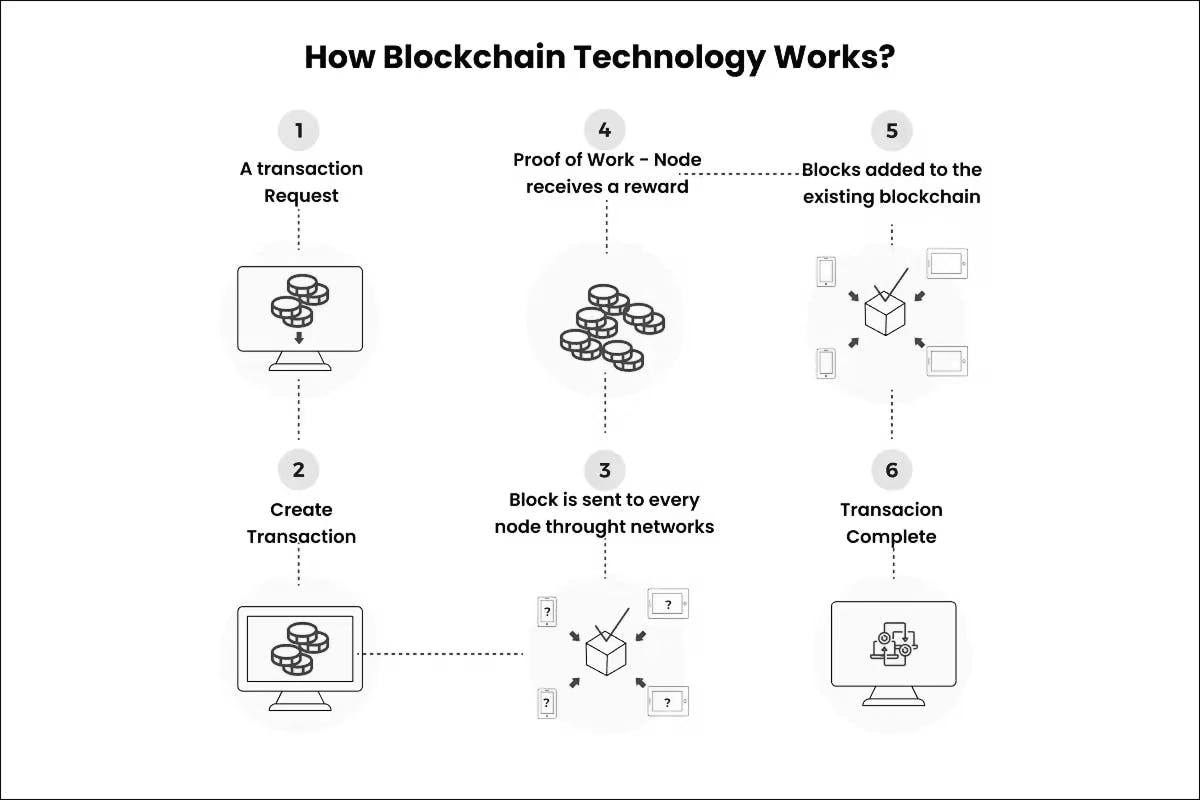
Once most of the nodes agree that the transaction is real, it is accepted. After then, a new block is made with that transaction and any other transactions that are still open.
Every block includes:
This link creates an unbreakable chain. The entire chain would be destroyed if someone attempted to modify a transaction in a previous block since the hash of that block would change.
This characteristic makes it clear that the ledger has not been tampered with. Any unauthorized changes become immediately visible and are rejected by the network.
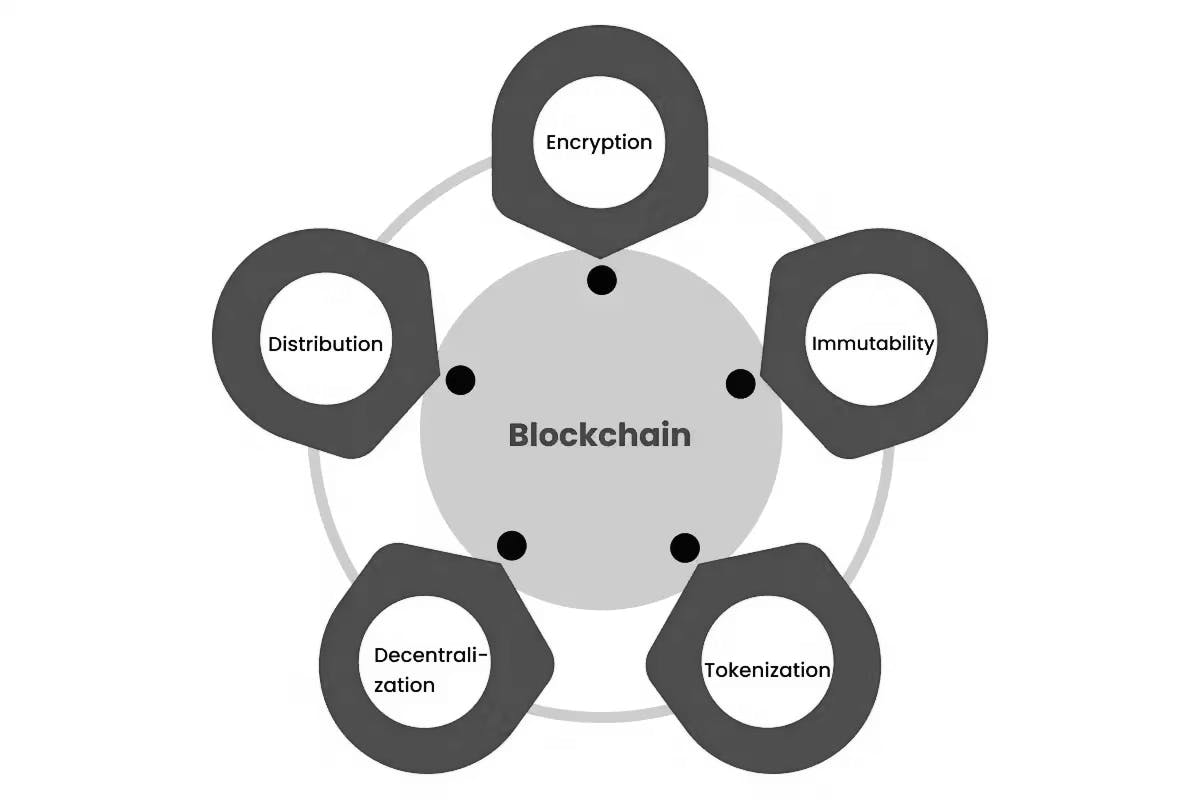
A number of fundamental characteristics set blockchain apart and make it revolutionary:
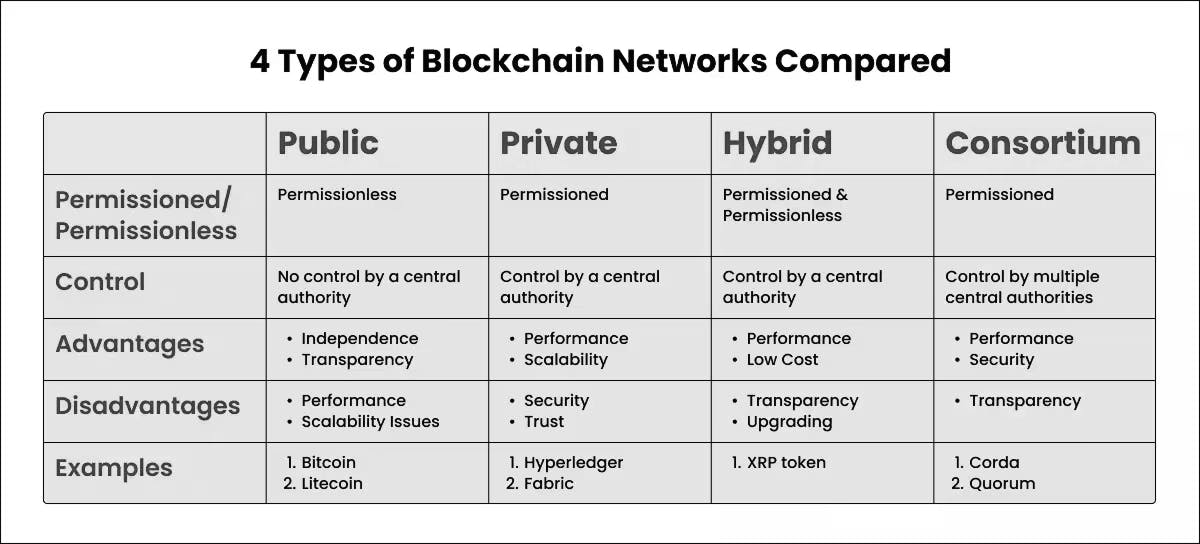
Various classifications of blockchain networks are present, each providing distinct benefits and compromises contingent upon the specific application.
Blockchain has developed as a revolutionary technology with applications across multiple sectors, thanks to its key qualities of immutability, transparency, security, and the elimination of intermediaries.
Banks, insurers, and capital markets are adopting blockchain for faster payment processing, trade finance, streamlined KYC/AML compliance, and efficient clearing and settlement of securities.
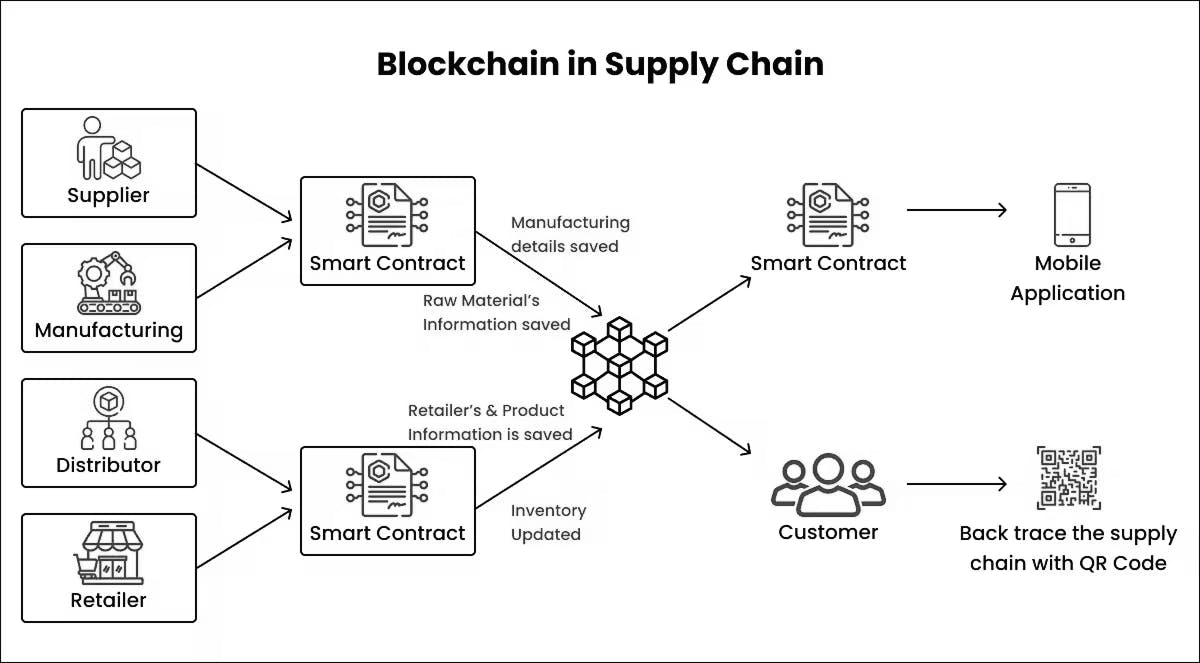
Blockchain lets you track the origin and final destination of goods and resources all the way through the supply chain. This makes it much easier to track things down, cuts down on fraud, and helps stop counterfeiting in worldwide supply networks.
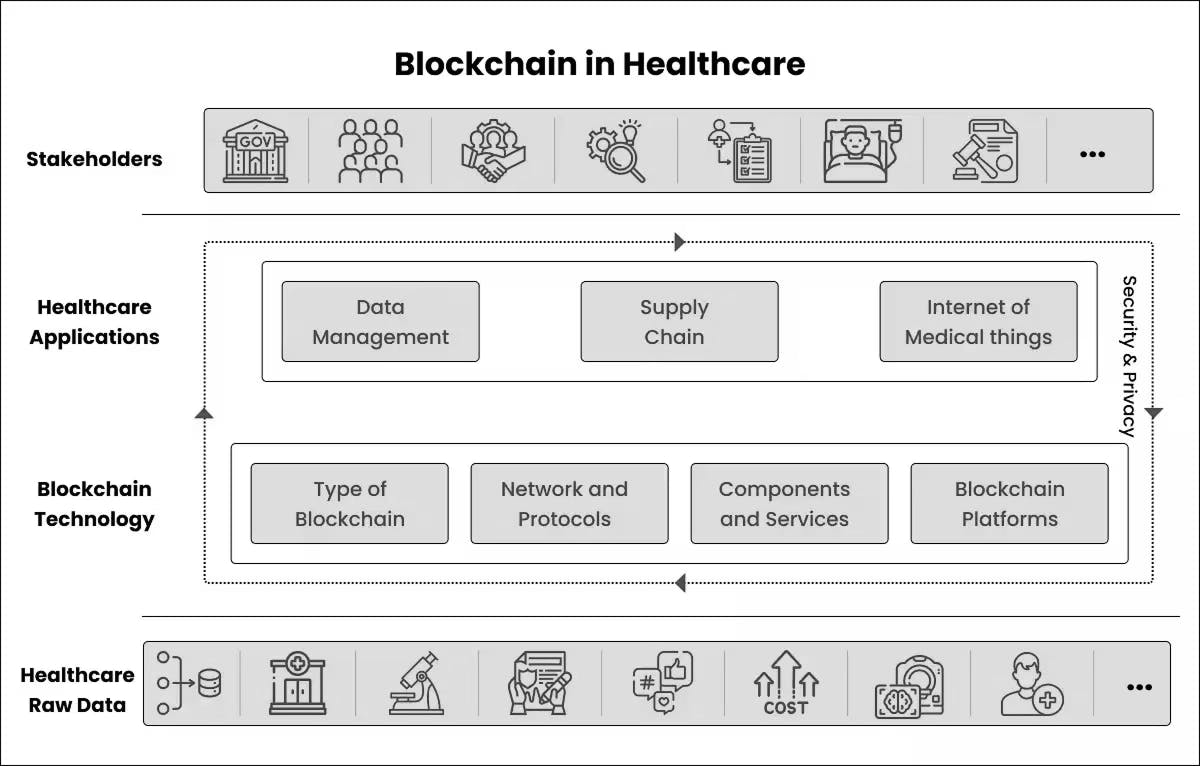
Secure sharing and transfer of medical records is a major application. Patients can control their data, and doctors can get to it safely. Blockchain also makes it easier to manage clinical trial data and pharmaceutical supply chains.
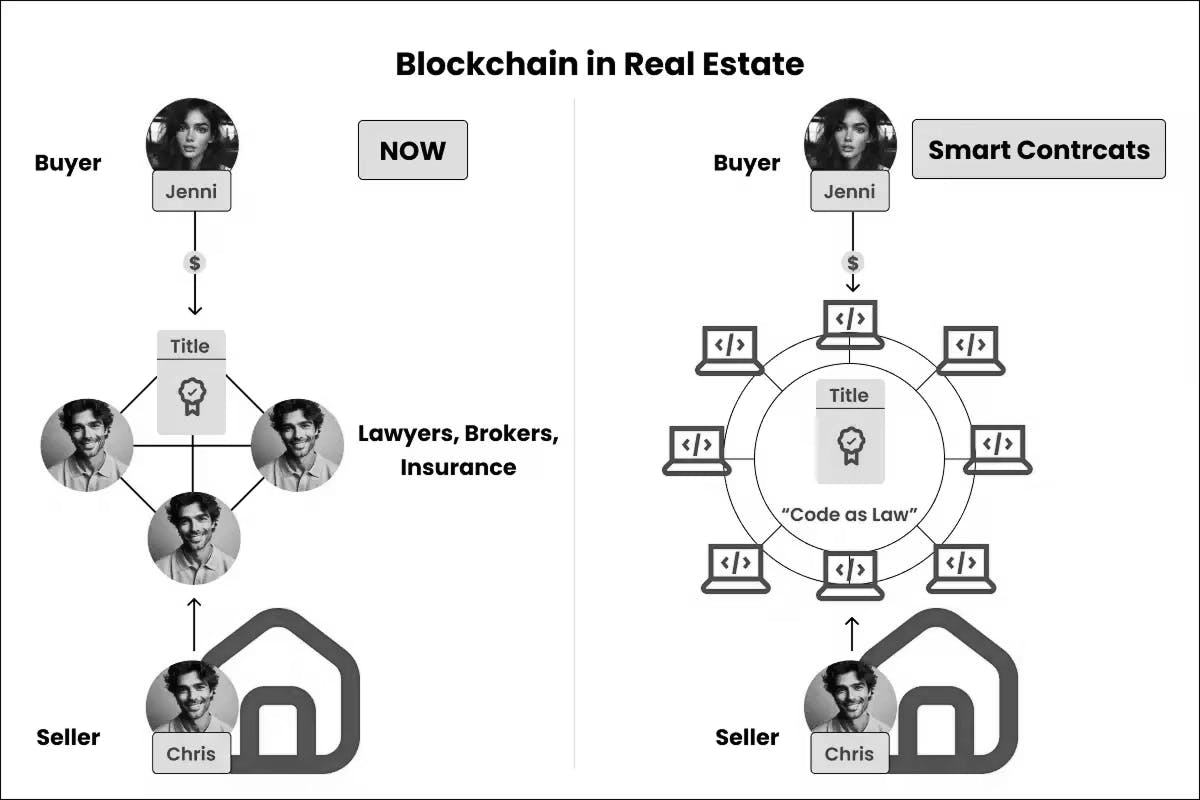
Immutable property title registries can eliminate fraudulent claims and ownership disputes. Smart contracts enable automated rent collection, utility payments, and even fractional ownership of assets.
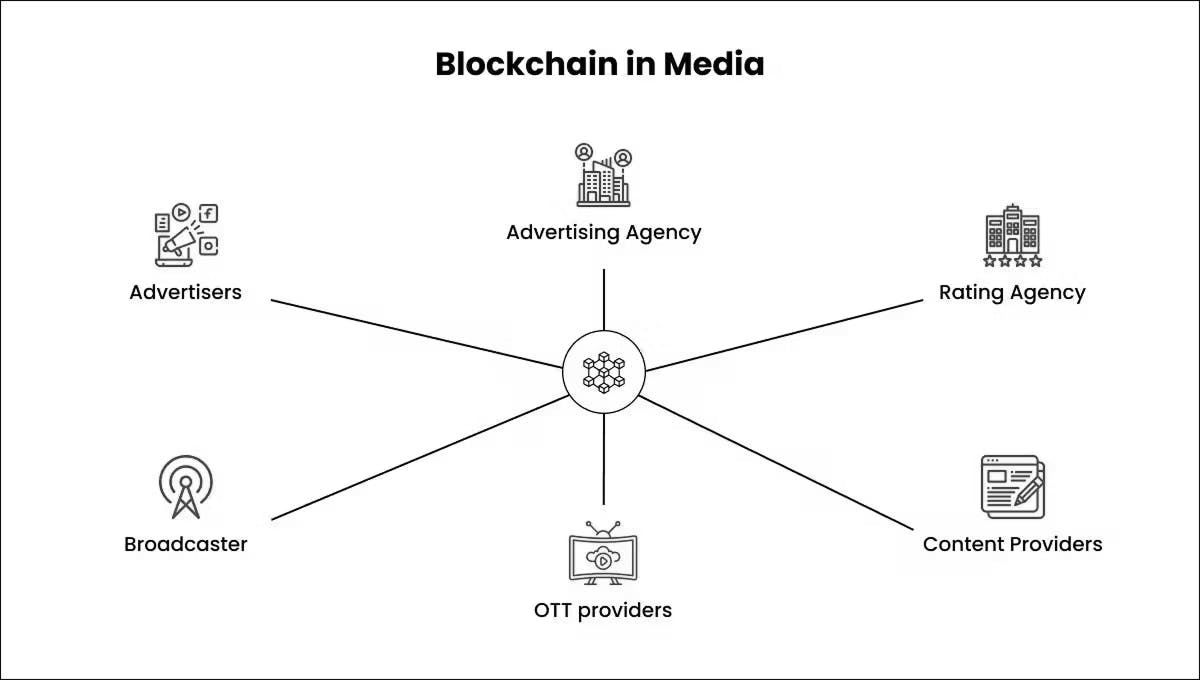
Blockchain helps with digital rights management, which keeps creators in charge of their work. It also makes it possible to pay royalties based on real use faster and more clearly.
Organizations adopting blockchain gain several transformative advantages:
Blockchain has a lot of potential for many organizations since it may make things more automated, efficient, secure, and clear, especially when there are many people involved in a transaction.
The technology is getting better and bigger, and more and more people are starting to use it every day.
There are still some big problems to deal with, such as energy use in proof-of-work systems, unclear rules, and connecting to current infrastructure. However, new technologies such as enterprise-grade platforms, improved consensus procedures, and layer-2 solutions are solving these issues.
If these obstacles are successfully overcome, blockchain has the potential to orchestrate the next major wave of digital transformation across countless domains.
Blockchain technology has been getting better and better for years. A lot of businesses are actively looking for experienced partners to assist them make the most of this new disruption.
One such leader paving the way is Codiste, a top blockchain development company.
Codiste is a remarkable partner with unparalleled experience and a track record of more than fifty completed projects.
Codiste helps enterprises build customized blockchain solutions across a wide range of sectors by leveraging strong technical understanding and strategic insight.
Codiste is a reliable blockchain firm in the US that assists clients in a lot of various scenarios by making things more clear, building trust, automating chores, and making things run more smoothly.
Working with seasoned experts like Codiste can hasten your transition into the blockchain-powered future, regardless of whether you're just starting out or are prepared to implement enterprise-grade technologies.



Every great partnership begins with a conversation. Whether you’re exploring possibilities or ready to scale, our team of specialists will help you navigate the journey.