


The AI landscape is rapidly evolving, and the connection between technology and value has become apparent. Technological application is not necessarily enough; results and business outcomes do matter. The objective measure of success for Generative AI(GenAI) has been how it enables enterprise strategies and drives tangible value. Organizations are scaling and learning from their GenAI pilots by effectively integrating AI tools into their core processes to develop comprehensive development strategies.
After all the hype over artificial intelligence (AI), the value is hard to find. CEOs have authorized investments, hired talent, and launched pilots—but only 22% of companies have advanced beyond the proof-of-concept stage to generate some value, and only 4% are creating substantial value. BCG
The discourse around GenAI has shifted from raw excitement to a more nuanced and critical evaluation of its impact on business, followed by the outcomes. Now, organizations are more focused on tailored GenAI tools—like small language models (SLMs)—for more targeted needs while exploring the rise of AI agents to redefine interactions within their digital environments.
The transformative potential of generative AI spans multiple industries, from healthcare’s improved diagnostics to financial services’ enhanced risk assessment and manufacturing’s optimized quality control. Organizations that have implemented GenAI strategically have reported significant productivity gains and cost reductions, though the success entirely depends on realistic expectations and proper digital transformation implementation frameworks. Enterprise AI plays a crucial role in large businesses by managing complex workflows, addressing data governance, and enhancing operational efficiency. In this guide, we will see all the essentials and implementations of GenAI in business to get the outcomes that can make an impact.
What do people mean when they say “generative AI?” The answer would be ChatGPT and its counterparts, but to your surprise, it goes way beyond that.
Are they talking about the ML models that can learn to make a prediction based on data? Well, think of this in a more modified and updated way: this is a machine-learning model trained to create new data. Here, the catch is that a GenAI system learns to generate more objects that look like the data it was trained on.
Artificial intelligence technologies encompass both general AI applications and enterprise AI. While general AI applications focus on specific tasks, enterprise AI is designed for complex business environments, integrating AI across multiple processes. GenAI, a subset of these technologies, showcases the ability to create new content using advanced machine learning models.
With each passing year, these systems have been trained as deep-learning models that can take raw data — say, the number of books your neighbourhood library might have — and then these models will learn to generate statistically probable outputs when prompted through data collected from each book. At times, generative models can encode a simplified representation of their data at a higher level and draw a new work similar to the original data but not identical.
The Generative models of the past were used in statistics to analyze numerical data. Still, with the rise of deep learning, extending their utility to process complex data, speech, images, and other possibilities is possible.
Trivia —much of what we think of today as generative AI started with variational autoencoders, or VAEs, introduced in 2013. VAEs were the first deep-learning models widely used for generating realistic images and speech.
Industry analyst Gartner projects more than 80% of organizations will have deployed or used GenAI application programming interfaces (APIs) by 2026 - Gartner
But do you know how this process of identifying ginormous amounts of data and then creating an outcome out of it works.
Well, here’s the answer: for the most part, GenAI operates:
They use foundation models trained on massive, unlabeled datasets to predict sequences like text, images, or code. These compute-intensive models, including LLMs and multimodal models, generate content autonomously. Pre-trained models like Meta’s Llama-2 reduce costs by providing a ready-to-use foundation. Data analytics is crucial in this training process as it enhances efficiency and facilitates informed decision-making.
Tuning adapts foundation models for specific tasks. Fine-tuning uses labelled datasets to improve accuracy, while RLHF incorporates user feedback to refine outputs. These methods transform generalist models into application-specific tools.
These apps need regular evaluation and tuning to stay accurate. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) boosts performance by incorporating external, up-to-date information, ensuring transparency and relevance beyond the original training data.
As enterprises fervently use AI for various purposes, we have seen its rapid industry-wide implementation. This AI can generate marketing content, pitch documents and product ideas, create sophisticated advertising campaigns, and much more, but what is the technology behind this peculiarity? Let’s check
Here’s a clear breakdown of each type of GenAI technology:
Large Language Models (LLMs): These are advanced AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data to understand and generate human-like text. LLMs like GPT-4 can engage in conversations, write content, analyze text, answer questions, and help with tasks like summarization and translation. They work by predicting the most likely following words in a sequence based on their training data, making them useful for everything from customer service to content creation and data analysis.
Image Generation Models: These AI systems can create, edit, and modify images based on text descriptions or other images. Models like DALL-E, Midjourney, and Stable Diffusion can generate highly realistic or artistic images from text prompts. They work by learning patterns from millions of image-text pairs, allowing them to create new images that match specific descriptions or style requirements. Business applications include product design, marketing materials, and rapid prototyping. Additionally, data visualization plays a crucial role in interpreting the generated images, making it easier to present and understand the data effectively.
Code Generation: These specialized AI models are trained in programming languages and can help write, complete, and debug code. Tools like GitHub Copilot can suggest code completions, generate entire functions based on comments, and allow developers to work more efficiently. They understand programming syntax, best practices, and common patterns across multiple programming languages, making them valuable for software development and automation tasks.
Audio and Video Synthesis: These models can generate, manipulate, or transform audio and video content. They can create human-like speech, music, or sound effects for audio. Video synthesis models can generate new videos, edit existing ones, or transform still images into animated content. Applications include:
Business leaders lack a strategy aligned with business objectives, hence the need for a structured framework to strategically exploit and integrate its capabilities.
The few organizations that made successful progress realized how a holistic approach spans from initial proof-of-concept to pilots to embedding AI across the entire enterprise. This comprehensive rethinking of business operations is essential for true digital transformations beyond mere digitization of existing processes.
Their strategies are comprehensive and go beyond identifying potential use cases. They also address critical elements such as articulating the general ambition, cultivating the right internal culture and workforce, defining execution plans, and maintaining an evolving roadmap as technology advances. Thus, the adoption process is a short-term project but an ongoing journey.
In this chapter, we will learn from that structured understanding by outlining a practical framework to synchronize an organization’s digital transformation with AI initiatives and its commercial vision and goals.
A GenAI framework is crucial to business strategy because it leads to a clear path that can help businesses. A well-defined framework will ensure all initiatives and business objectives are in sync, allocate resources efficiently, and address data privacy challenges, ethical considerations, and their impact inside and outside the organization.
Developing an AI framework becomes even more significant with its diverse technological applications, from healthcare to marketing and advertising, content creation, customer engagement, and many more. These developments thus prove the need for an approach that aligns with business objectives and moves them forward.
A Robust GenAI Framework Can:
An agile GenAI framework can foster an environment where the business can generate creative solutions and explore better opportunities with calculated foresight, keeping enterprises' technological pursuits aligned with its vision. Further ahead, we will see how this can help by understanding the entire framework.
Read more:
What is Generative AI?
How Generative AI Is Changing the Face of Customer Experience in Fintech
Developing Generative AI Responsibly with Security and Ethical Best Practices
Top 5 Podcast Use Cases of Generative AI in 2025
Top 10 Real Estate Use Cases of Generative AI in 2025
What is Style Generative Adversarial Networks?
The framework aims to provide business leaders a holistic approach to integrating transformative AI solutions into their strategies. It focuses on structured and sustainable implementation to achieve long-term competitive advantages and accelerate business outcomes.
The framework includes a comprehensive roadmap that outlines each execution step, covering all deployment aspects, including data collection, model training, deployment, and monitoring. It addresses data privacy, security, and ethical issues to ensure responsible and compliant AI initiatives. Evaluating and enhancing generative AI capabilities is crucial for assessing current technological maturity and identifying gaps, allowing organizations to set achievable targets and develop a roadmap for improving functionalities across various applications, including natural language processing and image generation.
Additionally, the framework enhances resource management and decision-making by helping businesses identify necessary skills and expertise for different implementation stages, facilitating efficient team assembly and resource allocation.
A seven-step process to define your strategic vision of the intelligent enterprise
AI-powered enterprise solutions demand a clear vision that goes beyond technology adoption. This vision must articulate how AI can transform core organizational operations, provide better customer experiences, and improve the overall market position. The key is to think boldly yet practically about AI's role in your business future. Consider how it could revolutionize your product offerings, streamline operations, or create new business models. Your strategic aspiration shouldn't just focus on keeping up with competitors—it should define how you'll lead your industry through AI innovation. This vision becomes your north star, guiding all subsequent AI initiatives and investments.
Before embarking on any AI implementation, conducting a thorough assessment of your organization’s starting point is crucial. This means looking hard at your existing technological capabilities, data infrastructure, and talent pool. Evaluate your data quality and accessibility, as these form the foundation of any successful AI initiative. Additionally, consider the challenges posed by legacy systems, which can complicate the adoption of new technologies and lead to significant workflow interruptions. Simultaneously, analyze your competitors' AI initiatives and identify market gaps where AI could give you a competitive edge. This assessment phase isn't just about identifying weaknesses—it's about discovering unique opportunities where your organization's strengths could be amplified through AI adoption.
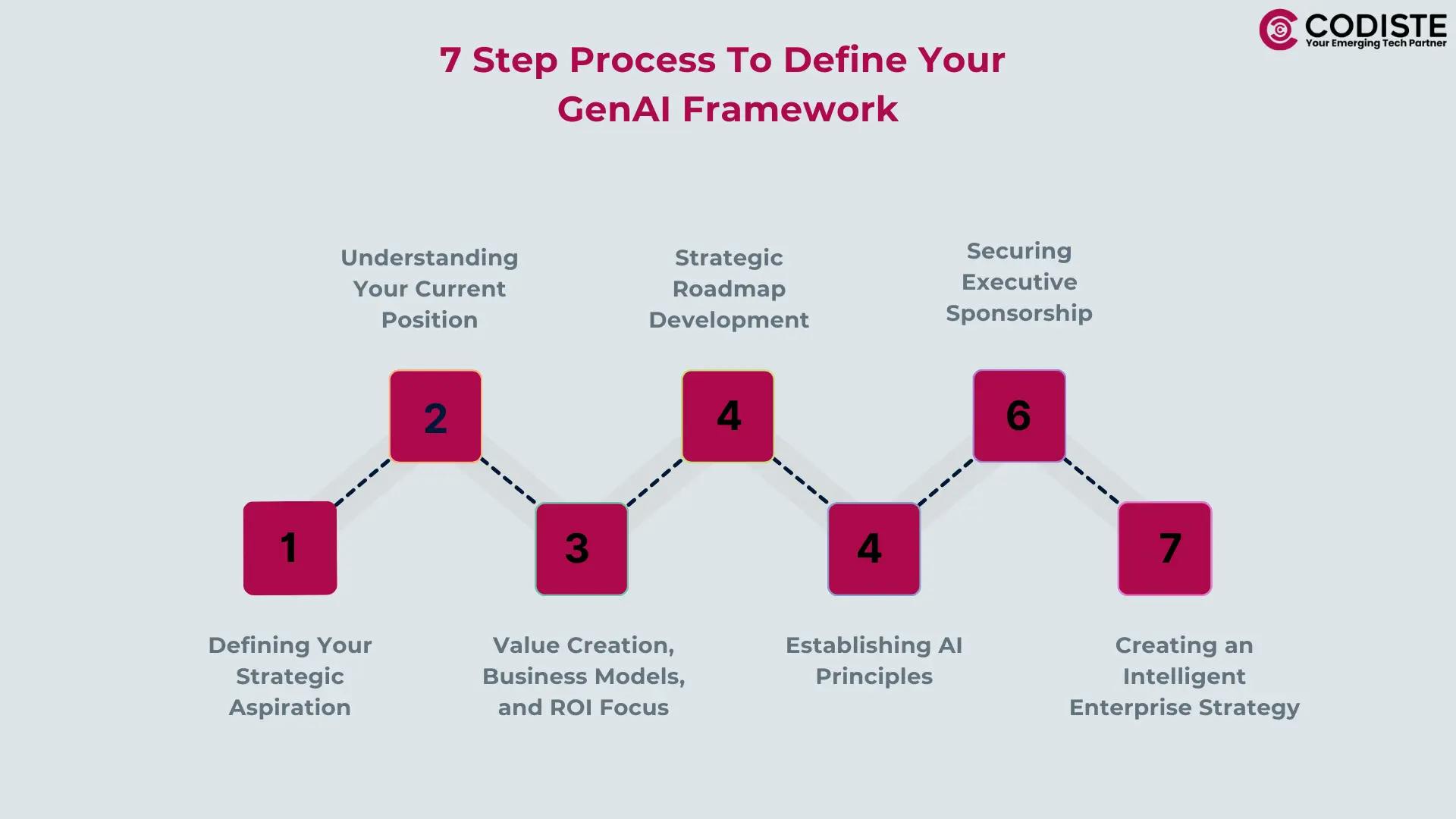
The success of your AI strategy hinges on its ability to deliver measurable business value. Begin by identifying areas where AI can drive immediate impact while building towards longer-term transformational goals. Focus on projects that can demonstrate clear ROI within the first year—these early wins are crucial for building organizational confidence and securing continued support for AI initiatives. Develop a balanced portfolio of AI projects, mixing quick wins with more ambitious, longer-term transformations. Remember that value creation isn't just about cost reduction; consider how AI can drive revenue growth, improve customer satisfaction, and create competitive advantages.
Your AI roadmap should be ambitious and practical, outlining a clear path from current capabilities to your desired future state. Structure it in phases, starting with foundation-building initiatives that address critical capabilities and data infrastructure. Follow this with targeted pilots that can demonstrate value and build organizational confidence. The final phase should focus on scaling successful initiatives across the organization. Make your roadmap specific enough to guide action but flexible enough to adapt to changing technologies and market conditions. Include clear milestones and decision points to help track progress and make necessary course corrections.
Developing clear principles for AI use is crucial for responsible and sustainable implementation. These principles should address ethical considerations, data privacy, algorithmic fairness, and transparency requirements. They serve as guardrails that ensure your AI initiatives align with your organization's values and compliance requirements. Your principles should be specific enough to guide decision-making while remaining flexible enough to accommodate technological evolution. Most importantly, they reflect your commitment to responsible AI use while fostering innovation and growth.
Success in AI transformation requires active and engaged executive leadership. This means more than just securing budget approval—it needs leaders who understand AI technology's potential and limitations. Your executive sponsors should be involved in setting direction, removing obstacles, and ensuring AI initiatives align with broader business strategy. Build a governance structure that enables quick decision-making while maintaining appropriate oversight. Regular executive reviews help ensure continued alignment and provide opportunities to adjust courses based on learning and results.
Your intelligent enterprise strategy brings together all elements into a cohesive whole. This strategy should detail how AI will be integrated into core business processes, how it will transform customer experiences, and how it will drive competitive advantage. Focus on building organizational capabilities that enable sustainable AI adoption—including data infrastructure, talent development, and change management processes. Your strategy should articulate clear success metrics while maintaining flexibility to adapt to new opportunities and challenges.
Implementing this framework requires patience, persistence, and a commitment to continuous learning. Start with manageable projects that can demonstrate value while building toward more ambitious goals. Focus on developing your team's AI capabilities through training and hands-on experience. Most importantly, maintain a clear focus on business value—technology should always serve your strategic objectives, not drive them. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your strategy ensures it remains relevant and practical as technology and market conditions evolve.
Elevate Your Business Processes with Advanced AI Solutions
Starting Today
Unlocking the true potential of generative AI for digital transformation is more than just deploying the technology. Integrating gen AI into business strategies is crucial for aligning with business goals and driving innovation. Other capabilities support an intelligent enterprise; organizations have an opportunity to fundamentally reimagine their data governance frameworks, talent model strategies, innovation processes, and core operations. This upgrade demands a holistic transformational approach guided by a comprehensive blueprint.
In this following section, we will see the practical implications of digital transformation with AI for getting businesses ready in key dimensions; although the technicals might vary, the fundamentals are universal; the vital thing to remember here is the commitment towards this implementation.
To effectively align your GenAI initiatives with broader business strategies and ensure sustainable execution, organizations can follow these key principles:
Generative AI should be adopted in line with overarching business goals, such as enhancing customer experience or driving innovation. Integrating digital technologies is crucial in this process, as they can significantly enhance customer experience and drive innovation. For example, a retail company might implement generative AI to create personalized product recommendations or deploy virtual assistants, directly contributing to customer satisfaction and engagement.
Identify specific business outcomes that generative AI can influence, ensuring investments focus on areas with the highest return potential. This alignment ensures that AI initiatives drive value where it is most needed and complement broader business agendas.
Regularly assess how generative AI initiatives meet strategic objectives and adjust strategies as necessary to align with evolving business goals.
Aligning these AI initiatives with business strategy while maintaining a sustainable execution workflow is crucial for delivering tangible value to business success. By focusing on strategic alignment, organizational capacity, and continuous innovation, companies can leverage generative AI effectively to enhance their operations and achieve their goals.
The increase in generative AI applications has caused people to have mixed feelings about it. Some are excited about its potential, while others are worried about its effects on jobs. GenAI will play a more eminent part in our present and future lives and careers, so addressing all the worries around this changing technology is essential.
As generative AI advances, concerns about its impact on employment are growing. The World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report 2024 highlights that, due to technologies like ChatGPT -4, approximately 69% of managerial tasks could be automated by 2027.
Additionally, it predicts that 64% of data processing tasks and 65% of reasoning and decision-making tasks may also be at risk of automation.
While some jobs may face disruption, the report emphasizes the importance of proactive measures to navigate these changes in the workforce.
Organizations must focus on reskilling and transitioning workers into new roles to harness the benefits of generative AI while mitigating job loss fears.
The prospect of significant workforce displacement has given rise to widespread anxiety and calls for policy intervention. Senior leaders are responsible for understanding and guiding organisations through this transformation, and there's one crucial aspect they must not overlook: human-centred AI.
As generative AI transforms industries, it raises critical questions about workforce displacement and societal impacts. Senior leaders are responsible for guiding their organizations through this change by focusing on human-centred generative AI. This approach emphasizes designing and deploying AI systems to augment human capabilities rather than replace them. The goal is to foster a future where generative AI benefits employees and society, driving inclusivity, innovation, and equitable growth.
Human-centred AI is vital for three key reasons:
Educate employees and stakeholders on how generative AI works, its limitations, and its potential to enhance—not replace—their roles.
Host workshops, seminars, and training sessions to foster a culture of understanding and collaboration.
Adopting human-centred AI offers significant benefits:
Generative AI is a powerful tool that can revolutionize industries when designed to prioritize human needs and values. Leaders must embrace human-centred, generative AI to ensure this transformation is inclusive, ethical, and sustainable.
Organizations can drive innovation while safeguarding societal progress by fostering trust, enabling workforce adaptability, and emphasizing collaboration between humans and machines. Together, we can build a future where technology and humanity advance hand in hand.
Integrating generative AI into business processes presents significant opportunities but raises critical ethical considerations. As organizations adopt these technologies, leaders must prioritize responsible implementation to avoid potential harm. Here's a concise overview of the key ethical concerns and the importance of using generative AI responsibly:
Looking for more in-depth AI development knowledge?
As generative AI continues to evolve, leaders must prioritize ethical considerations in its deployment. By embedding ethics into the core of their strategies, organizations can harness the power of generative AI responsibly, ensuring it serves to uplift humanity rather than cause harm. This commitment mitigates risks, fosters innovation, and builds trust within society.
When investing in generative AI, business leaders often face challenges in moving beyond the proof-of-concept (PoC) stage due to uncertainty in quantifying ROI. A multi-stage approach is essential, beginning with identifying clear use cases tied to measurable outcomes.
Leaders must adopt a value-centred framework to evaluate whether to build or buy solutions, ensuring alignment with business objectives and realistic ROI expectations. This proactive approach helps organizations harness their potential while staying grounded in practical, quantifiable returns.
Generative AI offers transformative potential but requires a structured approach to realize its value. Here's a concise guide for businesses to implement and invest in it effectively:
Evaluate Operational Expenses (OpEx) across departments to identify areas where GenAI can enhance efficiency. Estimate potential savings by applying efficiency gains to the quantifiable portion of OpEx.
Conduct an assessment to identify operational challenges and aspirational objectives that generative AI can address. Engage with management to create a clear landscape of opportunities, noting that some use cases may benefit multiple departments.
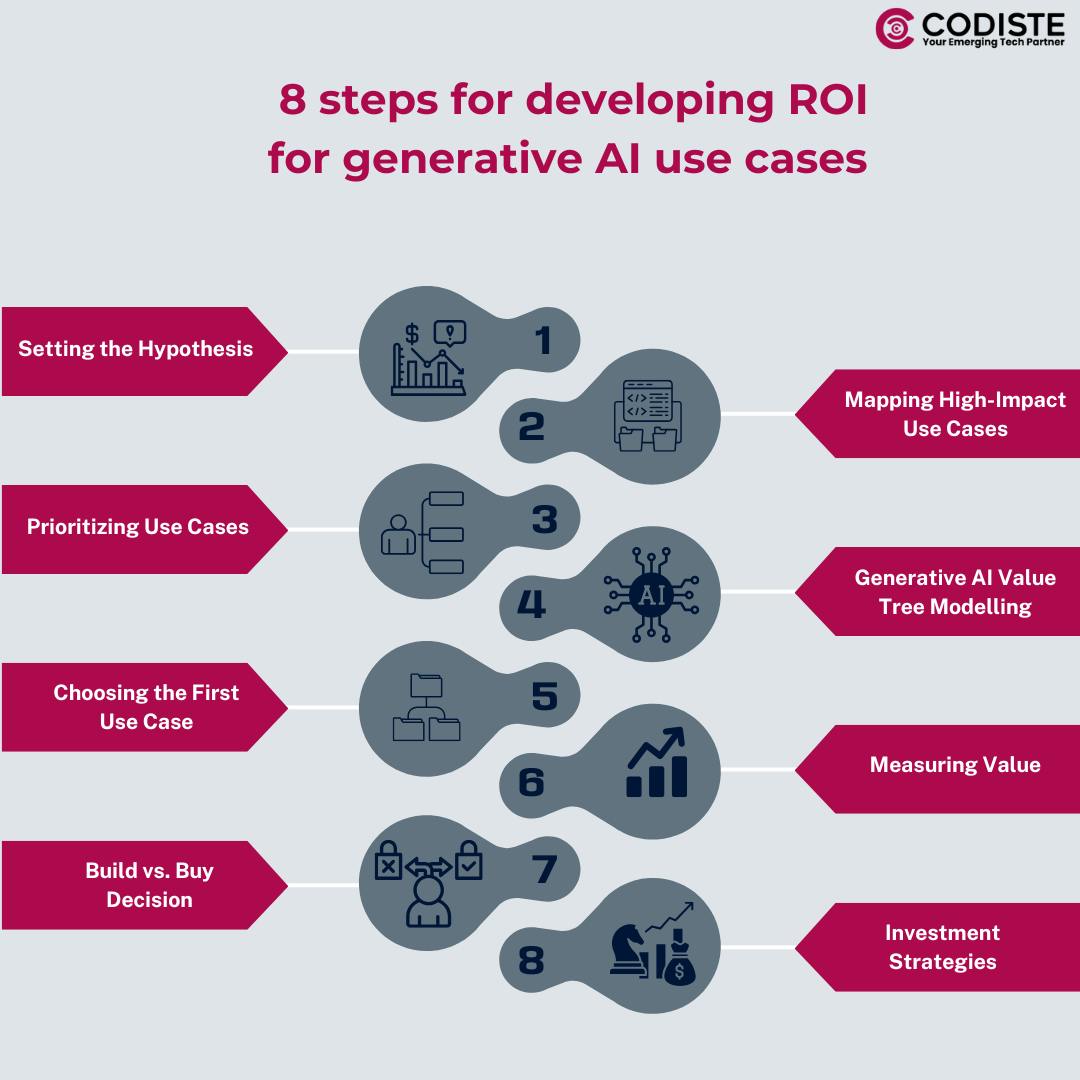
Secure operational buy-in by discussing business priorities and identifying 'quick wins' using a two-by-two impact-feasibility matrix. This helps in ranking potential generative AI use cases.
Develop a value tree to quantify potential ROI and total cost of ownership (TCO) for each solution. This model helps stakeholders understand the components contributing to ROI and supports investment decisions.
Match management's gut feeling with financial insights to select the most impactful use cases. Repeat modelling using bottom-up analysis to substantiate efficiency gains against baseline performance.
Establish clear metrics aligned with strategic objectives, such as productivity gains, cost savings, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, innovation, and compliance. A holistic approach combining quantitative metrics with qualitative assessments is crucial for understanding the impact of AI.
Use a framework to evaluate whether to buy or build generative AI solutions based on core competencies, cost, time to market, customization needs, data privacy, integration requirements, and market availability.
In a tightening economy, leaders should prioritize high-potential initiatives for piloting and scaling while balancing short-term returns with long-term advantages. Consider phased approaches, partnerships with tech companies, in-house innovation studios, or cloud-based solutions to maximize ROI and ensure sustainable growth.
By following these structured steps, organizations can effectively navigate the implementation complexities while optimizing their generative AI investments for future success.
Leverage Data Prediction To Make Better Choices
As GenAI technologies, large language models (LLMs), advance rapidly, they bring significant risks that organizations must address to ensure responsible and ethical use. Here are the primary risks associated with it:
GenAI can produce highly realistic text, enabling the spread of false narratives, conspiracy theories, and fake news on a massive scale. This undermines trust in institutions and erodes public discourse.
These systems can generate harmful code based on simple prompts, including viruses and malware. This capability allows even non-technical users to execute cyberattacks, posing security threats.
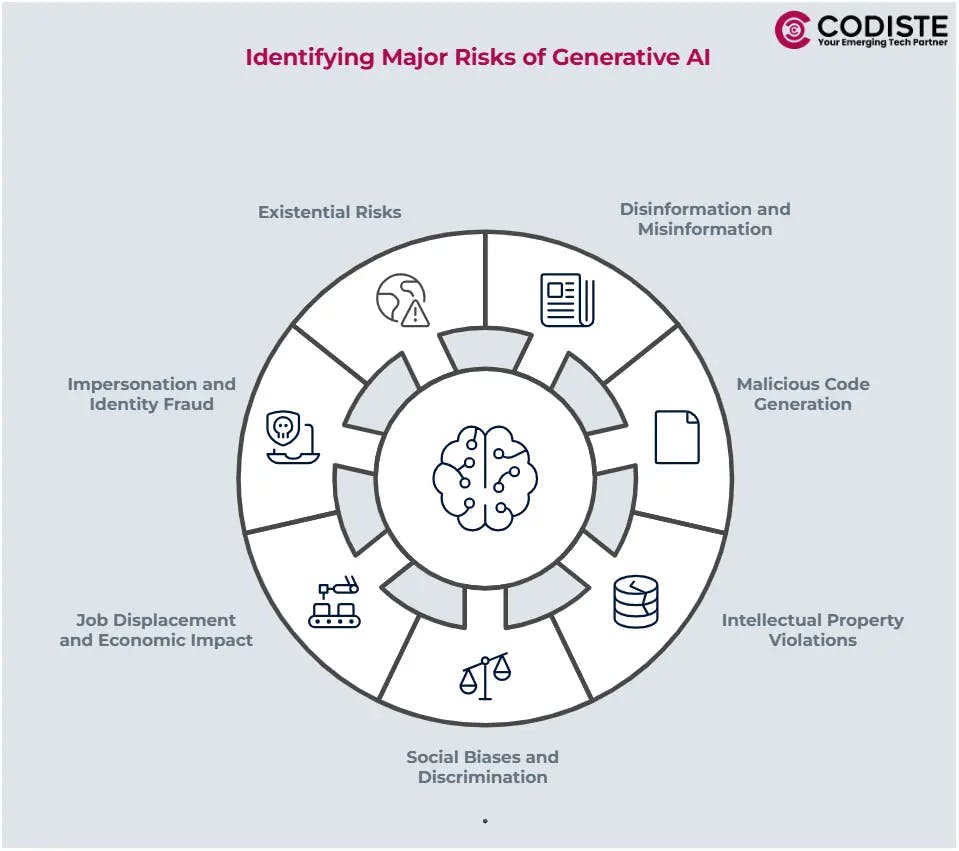
Facilitating mass plagiarism and copyright infringement by recreating proprietary works. This raises complex legal issues surrounding ownership and intellectual property rights.
Despite efforts to mitigate biases, generative models can perpetuate societal prejudices found in their training data, leading to the generation of hate speech or discriminatory content.
The automation potential of GenAI threatens job security across various sectors, potentially leading to technological unemployment and requiring society to redefine work.
The ability to mimic writing styles raises concerns about identity theft and scams, as it can create deceptive communications that appear authentic.
Although speculative, there are concerns that if AI surpasses human intelligence in cognitive tasks, it could lead to uncontrollable outcomes or concentration of power among a few elite entities.
Organizations must establish robust governance frameworks, ethical guidelines, and technological safeguards to mitigate these risks while balancing fostering innovation and protecting against potential negative impacts.
A proactive approach ensures that the GenAI is developed safely and beneficially for society.
AI is not a substitute for human intelligence but a tool to amplify human creativity and ingenuity - FEI-FEI LI, AI RESEARCHER AND PROFESSOR.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it's clear that GenAI is not just a fleeting trend—it's a transformative force reshaping the business landscape. By understanding its underlying technologies, strategic frameworks, and the ethical considerations involved, business leaders can leverage artificial intelligence to drive innovation and create competitive advantages.
Are you confident enough to harness the transformative power of GenAI for your organization? Start by defining and aligning your strategic aspirations with a robust AI framework. Contact us today to explore how we can help you navigate this exciting journey and unlock the full potential of GenAI for your business. By embracing GenAI thoughtfully and strategically, you position your organization to survive and thrive in the evolving business landscape. Let's build a future where humans and AI can collaborate to drive success.




Every great partnership begins with a conversation. Whether you’re exploring possibilities or ready to scale, our team of specialists will help you navigate the journey.